Differences Between Mic Level and Line Level
Confused about the differences between mic level and line level? You’re not alone. Easily decipher both terms and approach your studio setup with newfound clarity.

Have you ever found yourself questioning what the differences between mic level and line level are? And why it has differing applications with your equipment? For the unfamiliar, it can be confusing (there are even sound engineers who debate these meanings). However, there are answers to be found which will help you approach your studio with confidence.
First, it’s important to know what dBV means. This is essential knowledge for anyone working in audio. dBV refers to decibels relative to voltage. In practical terms, it’s how strong a signal is within a circuit which determines the volume.
And for those looking for a quick answer, here you go...
TL;DR: Mic level and line level refer to the voltage level of an audio signal, with mic level being a much lower voltage than line level. Mixing them up can result in messy audio issues.
Mic Level and Line Level Differences
Mixers and audio interfaces have inputs labelled ‘line level’ and ‘mic level’, which can seem confusing to newcomers.
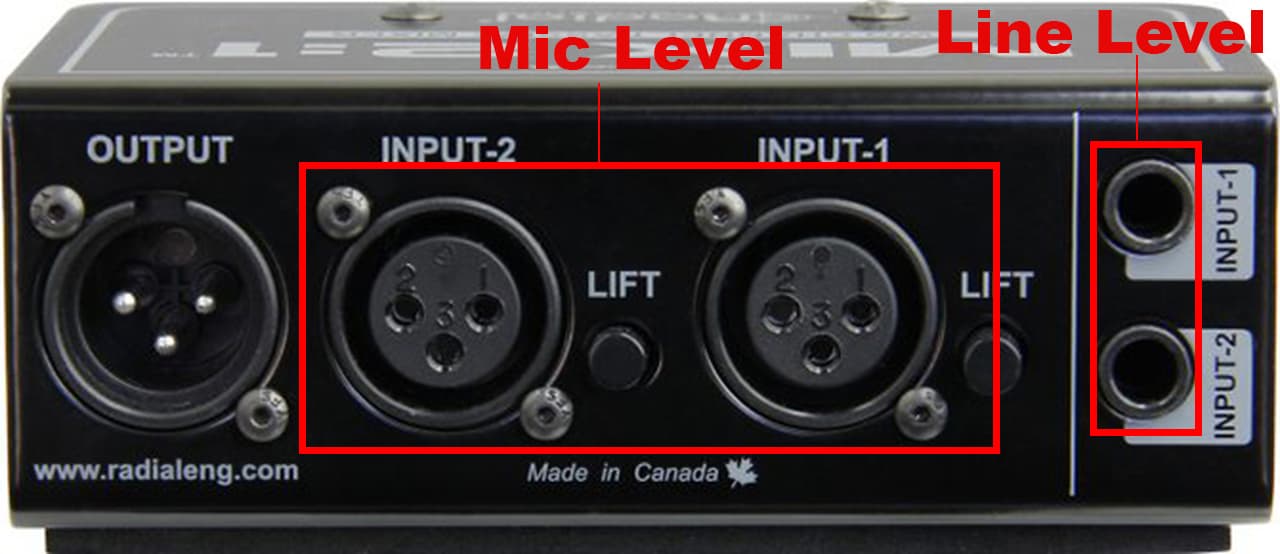

There aren’t huge discrepancies between the two, but they are vitally important for good audio. And could be the difference between your audio sounding incredible to a hot mess.
What is Mic Level?
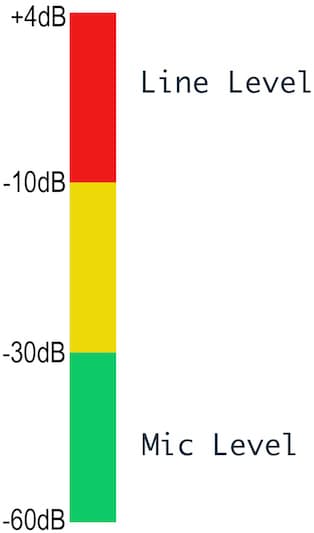
Mic levels are (as the name implies) for microphones. Typically, the audio level falls between -60dBV and -40dBV, which are equivalent to 0.001 Volts and 0.010 Volts respectively.
In human terms, that’s the level of voltage that is generated when a microphone picks up sound. It can vary depending on factors like the distance between the mic and sound source, and it’s volume. Mic level typically uses a female XLR connector, which can be an easy method for remembering the differences between mic level and line level.
What is Line Level?
Line level is the signal that flows through your recording equipment prior to being broadcast through speakers. This varies, depending on the equipment.
When using professional equipment such as mixers and other studio gear, line level is 4dBV. On consumer equipment like DVD and CD players, it is -10dBV. This is equal to 0.316 Volts and 1.23 Volts respectively. Another of the simple differences between mic level and line level is line level connections being through jack cable, rather than XLR.
Stopping Audio Distortion
No one likes bad audio. That’s why understanding the differences between mic level and line level are vital. On face value, they may seem simple, but they can cause issues for those unaware. Due to the extreme contrasts in voltage generated by both levels, if you mix up the two when connecting your equipment, it can produce unwanted results.
Connecting a microphone to a mixer through a line level input will result in your signal becoming practically inaudible, due to it not producing enough voltage. But, if you switch this and connect a line level source to a mic level input, the extra voltage will cause the signal to become overly loud and distorted.
Changing a Mic Level into a Line Level
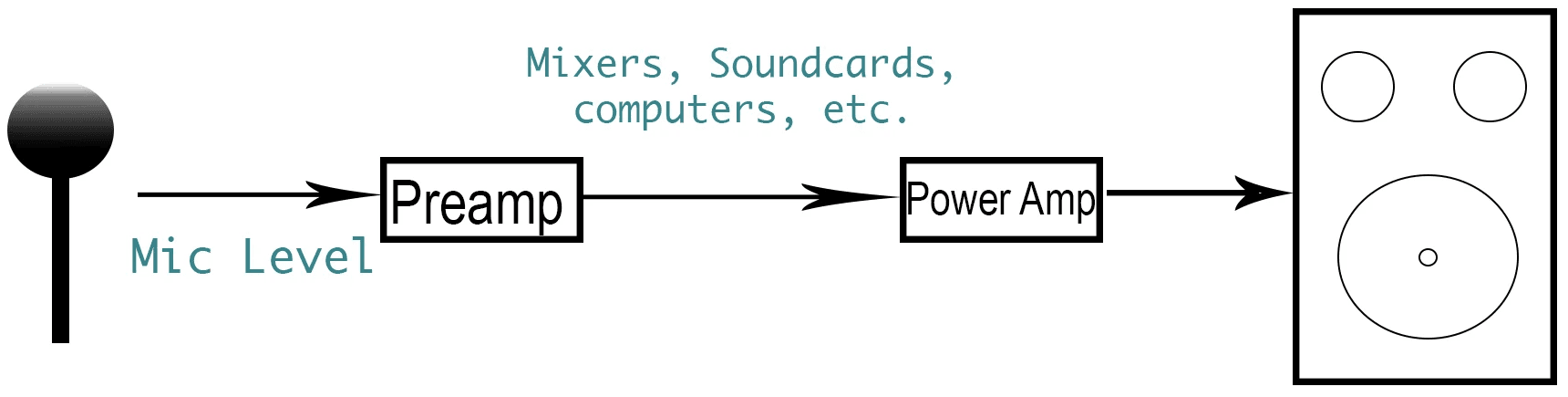
At times, you might not have the right tools for the job. But you work with what you’ve got. For those stuck with mic level, but in need of line level, there is a handy tool you can use to boost the signal. Broadcasters can use preamps like the Cloudlifter CL-1, which takes your mic level and boosts it by up to +25dB, making it easy and convenient to get line level.
Quick Tips for Beginners
Not everyone is a whizz when it comes to audio equipment. But that’s OK. For your reference, here are some handy audio tips worth taking note.
- Mic-level is a female XLR connector.
- Live-level is an RCA jack, 1/4″ phone jack, or 3.5 mm phone jack.
- Even if connectors fit, don’t assume everything will sound good. Always check levels.
- When mic level inputs are your only option, but you need line level, use a preamp.
- Microphone sound quiet? Check the user manual or online for the recommend dB.
Always Sound Your Best
Differences between mic level and line level aren’t vastly huge, but can cause serious issues for those unaware. Hopefully, you can now approach your studio with a feeling of confidence to produce quality audio to a professional standard.
Have you mixed up mic level and line level? Still not sure what the differences are? Let us know in the comments below. And for more helpful audio tips, you’re already in the right place.